SSH and SCP
Different examples to use ssh command
1. ssh command to connect to a remote machine
$ ssh IP_address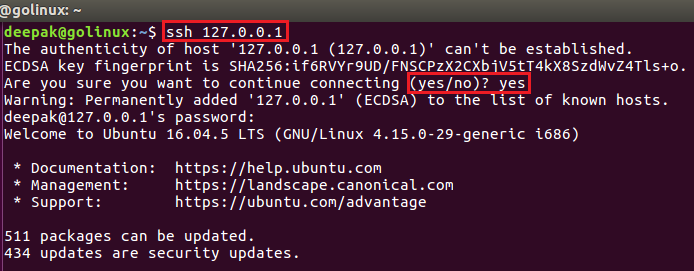
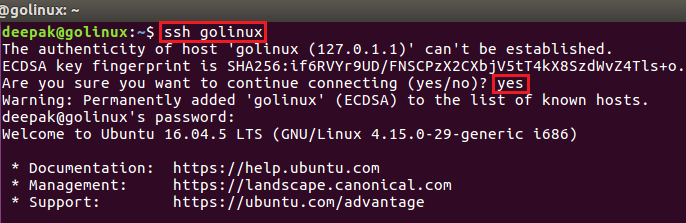
2. Login with a different user in SSH connection using ssh command
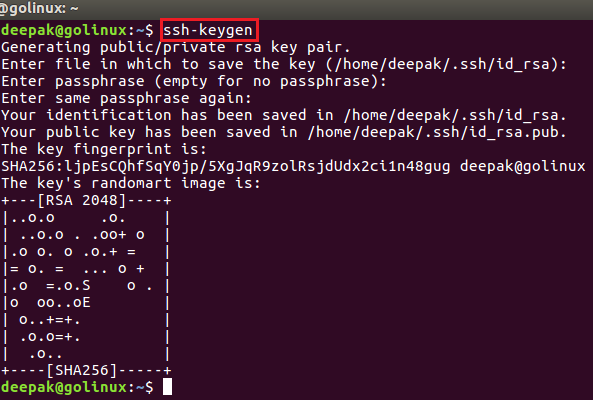
3. ssh command to generate SSH keys
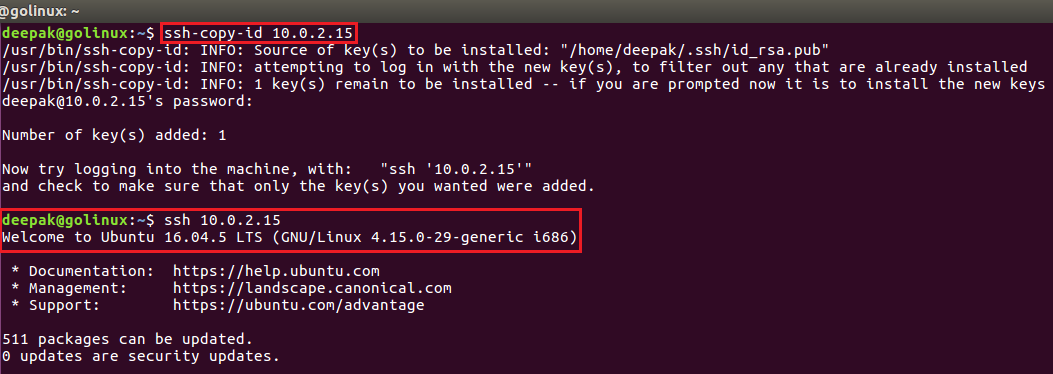
4. ssh command to copy public SSH key to a server
How scp command works (syntax)
Different examples to use scp command
1. scp command to copy a file from local to remote host
2. scp command to copy a file from remote to local host
3. Transfer files between two remote hosts with scp command
4. scp command to copy files and directories recursively
5. Display verbose output for scp command
PreviousIn-Process Memory Injection - PowershellNextSSH Key Predictable PRNG (Authorized_Keys) Process
Last updated